Solar energy is the energy obtained by capturing light and heat emitted by the sun.
Radiation power varies by time of day, weather conditions and latitude.
It can be assumed that a good surface radiation value is about 1000 W / m².
This power is known as irradiance.
Radiation is usable in direct and diffuse way, or the sum of both components.
Direct radiation comes directly from the solar focus, without intermediate reflections or refractions.
The diffuse is issued by the daytime sky thanks to the multiple reflection and solar refraction phenomena of the atmosphere, clouds and other atmospheric and terrestrial elements.
Direct radiation can be reflected and concentrated for use, while it is not possible to concentrate the diffused radiation coming from all directions.
Albedo radiation is reflected by the bodies located around the surface on which we want to assess the radiation.
The amount of energy due to sunlight direct radiation an exposed surface can intercept depends on the angle between the ray and the surface in question.
If the surface is perpendicular to the rays, this value is maximum, decreasing as the angle does.
The intensity on the surface varies in the same proportion as energy does.
This tilt effect is the reason why sunlight heat much more up at noon than in early morning or late afternoon.
It is also the reason why high-latitude regions (near the poles) received much less energy than the closest to Ecuador.
Solar coordinates used to determine Sun position referred to the horizontal plane are two:
• Solar Height (h) which is the angle between the sun’s rays on the horizontal surface. The zenith angle is the rays angle with the vertical, that is, the complement of the height.
Solar height (northern hemisphere perspective)
• Azimuth (A) which is the Sun angle rotation measured on the horizontal plane through the ray projection on said plane and taking as origin the North if we are in the southern hemisphere.
By convention, the azimuth is considered negative when the sun is to the east (morning) and positive when placed to the west (after noon).
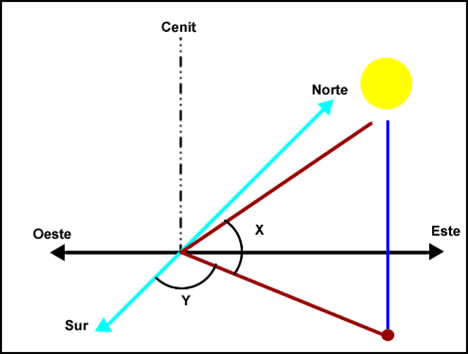
Azimuth
The theoretical number of sunshine hours is time length between sunrise and sunset.
In these 2 times the height of the sun is zero.
The number of sunlight hours depends on the geographical point considered and the time of year.
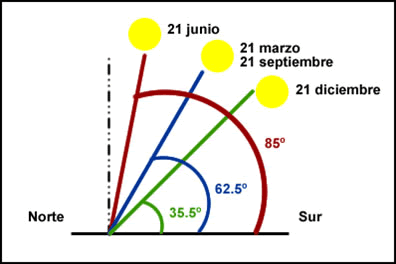
During the summer, the sun makes a very wide and high trajectory on the sky and is long over the horizon. The opposite happens in winter.

Path of the sun in different seasons (southern hemisphere perspective)
At solar noon (instant when the azimuth is zero), the sun elevation is maximum and shadows length minimun.
The shadow on the floor of a vertical rod coincide with meridian (South-North) direction, which must be accurately determined, for example, to correctly orient solar collectors or modules.
The most important factor influencing the amount of incident solar energy on a location or particular area is cloudy days ratio that occur each year.
This content is extracted from “Introduction to Solar Energy” ebook sold exclusively at Amazon.
Solar energy wherever you are with Sopelia.