We have already talked about flat solar collectors and vacuum tube collectors.
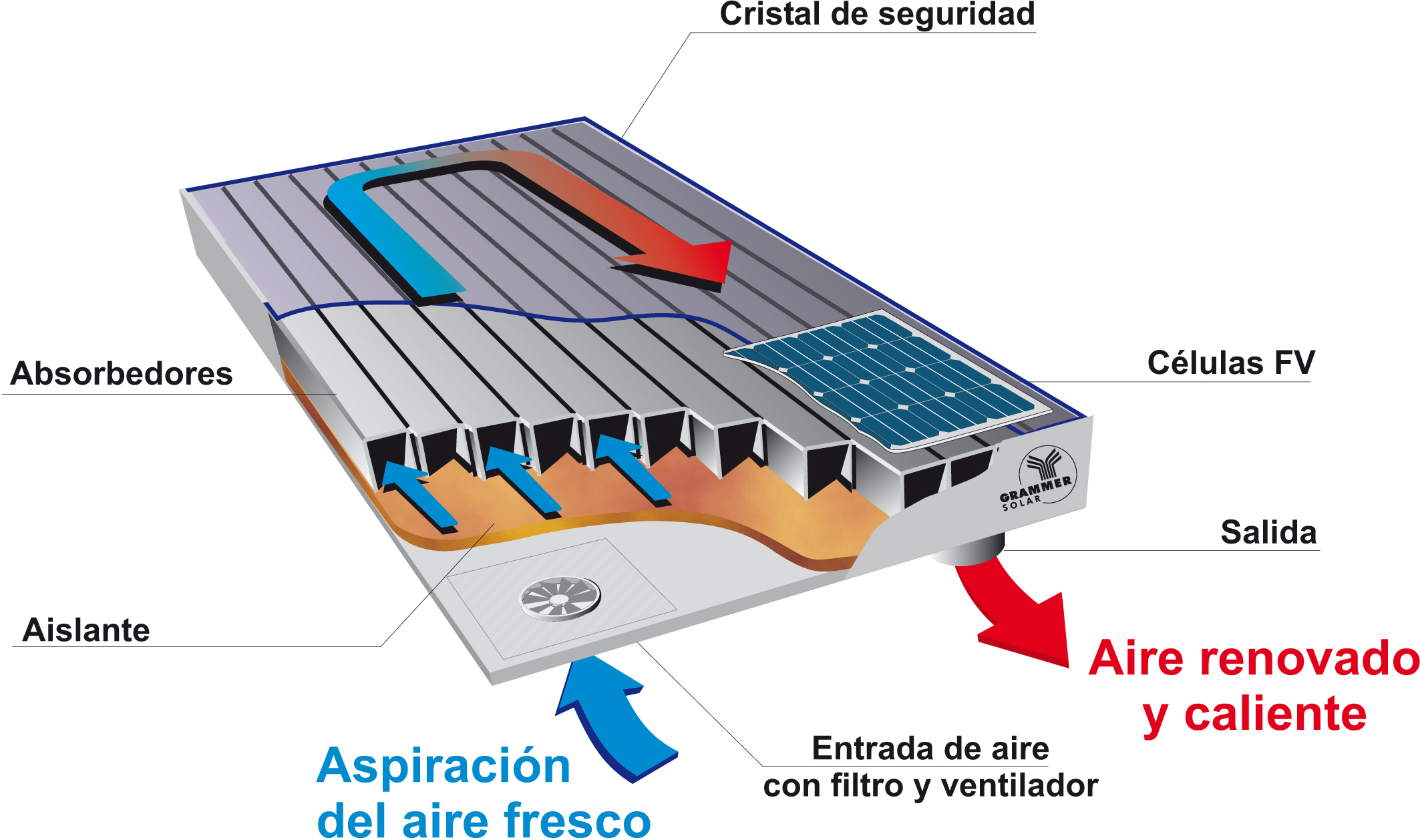
Air collectors are also found in collectors without concentration category.
They are flat and their main characteristic is to have air as heat transfer fluid.
They do not have a maximum limit temperature (convective processes have less influence on the air) and work better in normal circulation conditions, but in contrast they have a low heat capacity and heat transfer process between plate and fluid is not good.
Its main application is heating.
Externally it is not possible to distinguish an air collector from a water collector. It is in the absorber where greatest differences are found. It has a rough shape and lacks the classic pipe of water collector ducts. The air circulates freely on absorber surface collecting the heat that it transforms.
Being a technology that has not been widely disseminated until now, there is no standardized solar collector model and each manufacturer makes its own model.
There are also conical or spherical thermal solar collectors.
Their main characteristic is that they simultaneously constitute collection and storage unit.
Its catchment surface is conical or spherical with a same geometry glass cover. With this form it is achieved that illuminated surface throughout the day, in shade absence, is constant.
Their installation is simple, but they present water stratification problems and useful catchment surface is small.
Its main application is sanitary hot water in single-family homes production and in very benign climates, since large storage surface, weather exposed, causes great energy losses.
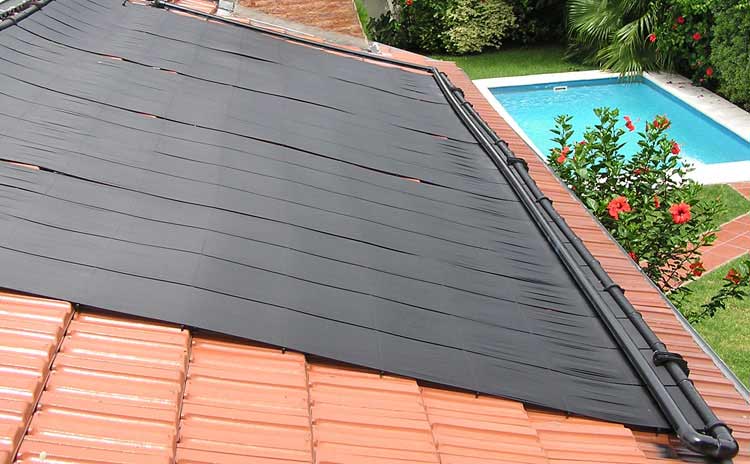
Finally, in collectors without concentration category, we find outdoor swimming pools solar collectors.
They are made of rubber, polypropylene or polyethylene; and incorporate in their manufacturing process substances that protect them from plastics natural tendency to degrade under ultraviolet rays action.
They also carry other additives to protect them from chemical agents used in pool water purification. They have an acceptable night frosts resistance.
They are used mainly to heat pools water and thus be able to prolong its use for several more months.
These collectors do not have cover, neither with housing nor with insulating material. They are constituted by naked plate collector. This is because working temperature will not exceed 30ºC in any case and at this low temperature, radiation and conduction losses are very small, making it possible to dispense with covers and insulation.
It is not necessary to use any type of heat exchanger or accumulator, because pool water flows directly through collectors.
They need a frame because they are usually not rigid, but they can also be placed directly on a roof, or even on the ground. By being flexible, absorb surface irregularities on which they rest.
These equipment enjoy an approximate 10 years lifespan. They need little maintenance and there is little risk of corrosion, as they are synthetic.

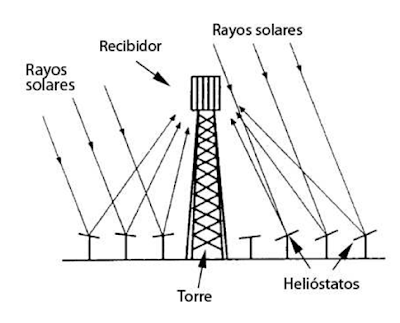
The second major group is that of solar collectors with concentration.
Its most common use is not at domestic level but in thermoelectric plants and facilities that work at medium and high temperature.
These collectors concentrate the solar radiation received in a very small surface receiving element (a point, a line).
Being smallest receiver and concentrated radiation, it allows a better solar energy absorption.
They are capable of providing temperatures above 300 ° C with good yields.
Concentration collector plants generate high temperature steam for industrial processes and to produce electricity.
There are concentration collectors of various types (tower, cylindrical-parabolic, Stirling engine).
Nevertheless, all of them have in common that they demand to be equipped, to be efficient, with a tracking system that allows them to remain constantly located in best position to receive the Sun’s rays throughout the day.
One of the drawbacks of most concentration collectors (and especially the cylindrical-parabolic) is that they only take advantage of Sun direct radiation, that is, they only take advantage of solar rays that actually hit their surface. They are not able, on contrary, to capture diffuse solar radiation.
Therefore, they are not convenient in climatic zones that, although they receive an acceptable solar radiation amount, are relatively cloudy. They are only effective in authentically sunny áreas.
This content was extracted from the Solar Thermal Energy Technical-Commercial Manual and is part of Solar e-learning.
All you need is Sun. All you need is Sopelia.
