Thermal solar collector is responsible for capturing solar radiation and converting its energy into heat energy.
A body exposed to the sun receives an energy flow Er and heats up.
Simultaneously, thermal losses occur due to radiation, convection and conduction, which grow as the body temperature increases.
There comes a time when thermal losses Ep equals the gains due to the incident energy flow, reaching the so-called equilibrium temperature:
Er = Ep
The equilibrium temperature of the collectors is usually between 100º and 150º C under normal conditions of use and for irradiation values in the order of 1,000 W / m2.
If it is possible to continuously extract a part of the heat produced Ee to take advantage of it as usable energy, the equilibrium conditions change:
Er = Ep + Ee
Ep is now smaller because a part of the energy received Er is tapped Ee.
The body has become a solar thermal collector.
If we want to increase Ee we have two options: reduce thermal losses Ep or increase energy flow Er.
First option involves collector design and construction improving in order to reduce losses.
For the second option is used the concentration technique, which by some optical system concentrates the solar flux on a smaller surface so that as the area decreases, the intensity increases.
In a solar collector the energy is extracted through a fluid called heat carrier.
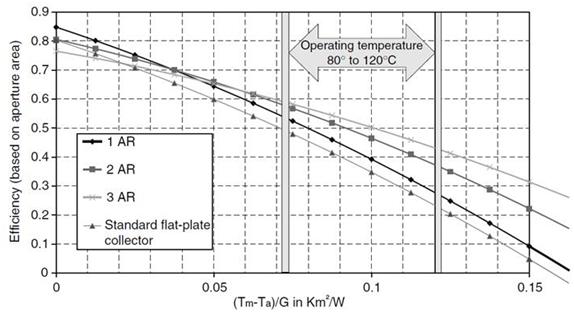
The greater the difference between operating temperature and ambient temperature, the greater the thermal losses and thus the lower energy amount that heat transfer fluid will be able to extract.
The collectors must be operated at the lowest possible temperature, provided that temperature is sufficient for the specific use in each case.
This is because collector efficiency decreases as the operating temperature increases.
Improved insulation helps thermal losses reduce.
Reflection losses are due to transparent cover that usually exists in almost all collectors.
It will be necessary to properly orient the collectors so that they receive the greatest radiation amount possible during the period of use.
The question: which is the best collector ?
A priori has no answer.
It will depend on system location and energy demand that is intended to be met.
There are many types of solar collectors, but there are two large groups: unconcentrated collectors and concentrated collectors.
Solar thermal collectors according to their working temperature:
1) Low temperatura
1.1) Flate: protected and not protected
1.2) Vacuum tubes: direct flow, heat pipe and solar concentrator CPC)
2) High temperatura
2.1) Parabolic Cylinder
2.2) Central receiver system
2.3) Parabolic disks
2.4) Solar chimney
3) Other collectors
3.1) Rubber
3.2) Spherical
3.3) Conical

In next posts we will analyze in detail each collector type.
This content was extracted from the Solar Thermal Energy Technical-Commercial Manual and is part of Solar e-learning.
Solar energy wherever you are with Sopelia.
